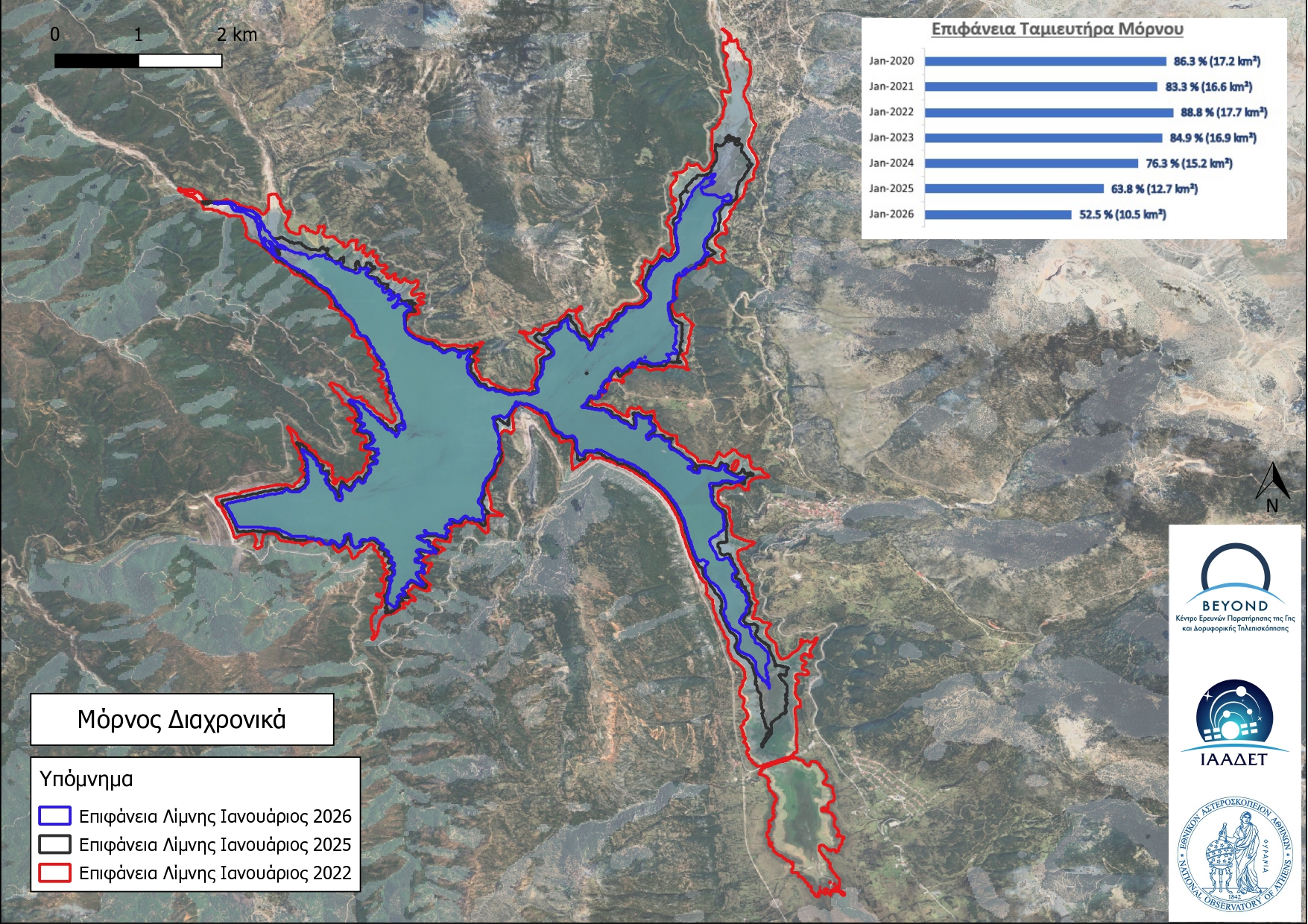
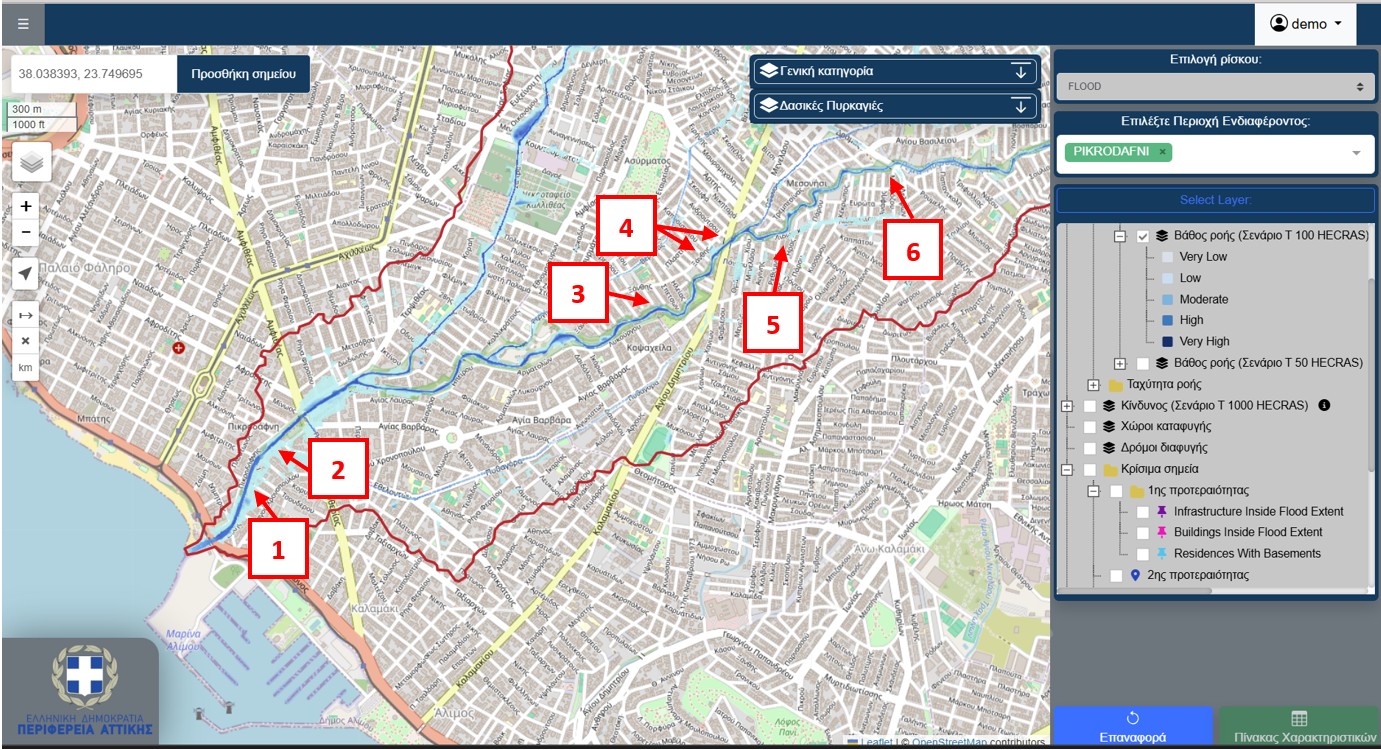
Στο πλαίσιο της συμμετοχής του Εθνικού Αστεροσκοπείου Αθηνών στη συνεδρίαση της Υποεπιτροπής Υδατικών Πόρων της Ειδικής Μόνιμης Επιτροπής Προστασίας Περιβάλλοντος της Βουλής, ο Δρ Ευάγγελος Γερασόπουλος, Αντιπρόεδρος του Δ.Σ. του ΕΑΑ και Διευθυντής του ΙΕΠΒΑ, καθώς και ο Δρ Χαράλαμπος (Χάρης) Κοντοές, Διευθυντής Ερευνών του ΕΑΑ και Επιστημονικός Υπεύθυνος της Επιχειρησιακής Μονάδας BEYOND εκπροσώπησαν τον φορέα και ενημέρωσαν τα μέλη της Υποεπιτροπής σχετικά με το θέμα της ημερήσιας διάταξης: «Πρόληψη και αντιμετώπιση πλημμυρικών φαινομένων: Οικοδομώντας την ανθεκτικότητα», την Πέμπτη, 26 Φεβρουαρίου 2026.