|
SWeFS: ΠΛΕΓΜΑ ΑΙΣΘΗΤΗΡΩΝ ΓΙΑ ΤΗ ΘΩΡΑΚΙΣΗ ΑΠΟ ΠΕΡΙΒΑΛΛΟΝΤΙΚΟΥΣ ΚΙΝΔΥΝΟΥΣ/SENSOR WEB FIRE SHIELD ΓΕΝΙΚΗ ΓΡΑΜΜΑΤΕΙΑ ΕΡΕΥΝΑΣ ΚΑΙ ΤΕΧΝΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ (ΓΓΕΤ), ΠΡΟΓΡΑΜΜΑ ΓΙΑ ΤΗΝ ΕΝΙΣΧΥΣΗ ΤΗΣ ΔΙΕΠΙΣΤΗΜΟΝΙΚΗΣ ΕΡΕΥΝΑΣ ΚΑΙ ΚΑΙΝΟΤΟΜΙΑΣ, GA : 01/164/6 2012-2015 77.000 (NOA Budget)/519.798 EUR (Overall Budget) |
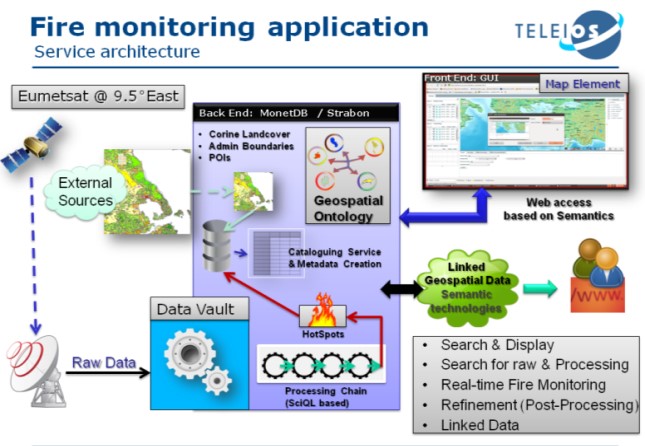
The project SWeFS consisted a complementary action that supported the further development of the innovative FIREHUB system of services of the BEYOND Center of Excellence , which offers real-time fire monitoring and burnt scar mapping applications; the FIREHUB system has awarded the Best Challenge Service award in the Copernicus Master's competition of 2014.
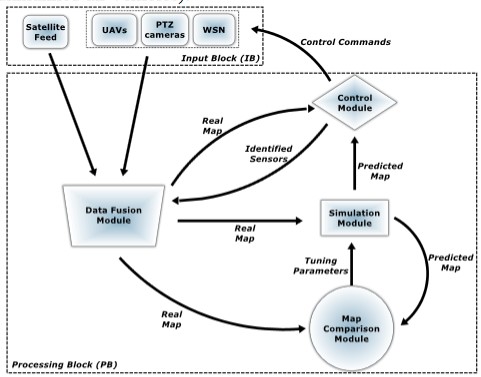
The SWeFS research project delivered a novel Sensor Web platform for dynamic data-driven assimilation (DDDAS) for securing the Wildland-Urban Interface (WUI) zones against environmental risks, and serious threat of forest fires in Greece. SWeFS called for multidisciplinary research in the areas of sensor networks, distributed vision systems, remote sensing, geographical information systems (GIS), data stream fusion, space-time predictive modeling and control systems. The research team of BEYOND Center of Excellence undertook the integration of satellite data in a multi-sensor system approach feeding the final decision with a multitude of evidences from sensor networks. The developed fusion architecture adopts a two-level fusion scheme, thus improving the reliability of the system w.r.t. fire detection. In the first level of fusion (data fusion), a statistical analysis was adopted for fusing data taken from in-field sensors and assigning a probability of fire occurrence to each of them. In the second level of fusion (information fusion), probability values about fire events from the first level were combined through approximate reasoning scheme like evidential theory (Dempster – Shafer) (doctoral thesis of Dr C. Kontoes).